Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Naoe, Takashi; Wakui, Takashi; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Teshigawara, Makoto; Haga, Katsuhiro
JAEA-Technology 2023-022, 81 Pages, 2024/01
In the liquid mercury target system for the pulsed spallation neutron source of Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), pressure waves that is generated by the high-energy proton beam injection simultaneously with the spallation reaction, resulting severe cavitation erosion damage on the interior surface of the mercury target vessel. Because the bubble of pressure wave-induced cavitation collapsing near the interior surface of the mercury target vessel with applying the large amplitude of localized impact on the surface. Since the wall thickness of the beam entrance portion of the target vessel is designed to be 3 mm to reduce thermal stress due to the internal heating, the erosion damage has the possibility to cause the vessel fatigue failure and mercury leakage originated from erosion pits during operation. To reduce the erosion damage by cavitation, a technique of gas microbubble injection into the mercury for pressure wave mitigation, and double-walled structure of the beam window of the target vessel has been applied. A specimen was cut from the beam window of the used mercury target vessel in order to investigate the effect of the damage mitigation technologies on the vessel, and to reflect the consideration of operation condition for the next target. We have observed cavitation damage on interior surface of the used mercury target vessel by cutting out the disk shape specimens. Damage morphology and depth of damaged surface were evaluated and correlation between the damage depth and operational condition was examined. The result showed that the erosion damage by cavitation is extremely reduced by injecting gas microbubbles and the damage not formed inside narrow channel of the double-walled structure for relatively high-power operated target vessels.
Nakayama, Shinsuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(12), p.1447 - 1453, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The d+Be neutron source is a candidate for transportable neutron source for on-site nondestructive inspection of infrastructure facilities such as bridges, tunnels and so on. The applicability of the d+Be neutron source to a transportable fast neutron source is explored by Monte Carlo particle transport simulations with PHITS and JENDL-5. The simulation results show that by increasing the shielding thickness by about 1.5 times, it is possible to realize the d+Be neutron source with the comparable performance to another candidate, the 2.5-MeV p+Li neutron source, at lower beam energy.
Koizumi, Mitsuo; Mochimaru, Takanori*; Hironaka, Kota; Takahashi, Tone; Yamanishi, Hirokuni*; Wakabayashi, Genichiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1042, p.167424_1 - 167424_6, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Nakayama, Shinsuke
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (133), p.88 - 99, 2022/10
The content of the paper that received the Paper Award of Atomic Energy Society of Japan in 2021 is outlined. Although the use of deuteron accelerator-based neutron sources has been proposed in various fields, deuteron nuclear database accurate enough to be applied to the design study of such neutron sources had not been developed. Under these situations, we had developed a deuteron nuclear database, JENDL/DEU-2020. It contains evaluated deuteron nuclear data for light nuclei (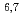 Li,
Li,  Be,
Be, 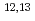 C), which are candidates for deuteron beam irradiation targets of the neutron sources. Evaluation of JENDL/DEU-2020 was performed by using the code system DEURACS with further modifications. In order to validate the accuracy of the database, simulations using the particle transport code were performed under various conditions with different target nuclides and incident deuteron energies, and the results were compared with the available experimental data. As a result, it was found that JENDL/DEU-2020 significantly improves the prediction accuracy of experimental data under a wider range of conditions than other nuclear reaction databases or the nuclear reaction models implemented in transport calculation codes.
C), which are candidates for deuteron beam irradiation targets of the neutron sources. Evaluation of JENDL/DEU-2020 was performed by using the code system DEURACS with further modifications. In order to validate the accuracy of the database, simulations using the particle transport code were performed under various conditions with different target nuclides and incident deuteron energies, and the results were compared with the available experimental data. As a result, it was found that JENDL/DEU-2020 significantly improves the prediction accuracy of experimental data under a wider range of conditions than other nuclear reaction databases or the nuclear reaction models implemented in transport calculation codes.
Iwamoto, Chihiro*; Takamura, Masato*; Ueno, Kota*; Kataoka, Minami*; Kurihara, Ryo*; Xu, P. G.; Otake, Yoshie*
ISIJ International, 62(5), p.1013 - 1022, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:32.54(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
Few-Body Systems, 63(1), p.4_1 - 4_6, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Intensive neutron sources using deuteron accelerators have been proposed for not only science and engineering fields but also medical applications. For the engineering design of such facilities, accurate and comprehensive nuclear data of deuteron-induced reactions are indispensable. However, it is difficult to meet the requirement by employing experimental data alone. Thus, theoretical model calculations play a key role in completing the necessary nuclear data by interpolation and extrapolation of experimental data. Under the above situations, we have been developing a code system dedicated for deuteron-induced reactions, called DEURACS. In the present work, calculations using DEURACS are compared with available experimental data and validation of the present modelling in DEURACS is discussed. Moreover, the importance of consideration of the breakup processes for accurate prediction of deuteron-induced reactions is also presented.
Nakayama, Shinsuke
JAEA-Conf 2021-001, p.65 - 70, 2022/03
Since deuteron is a weakly bound system consisting of a proton and a neutron, it easily breaks up and emits a neutron through interaction with a target nucleus. Utilizing this property, intensive neutron sources using deuteron accelerators have been proposed for not only science and engineering fields but also medical applications. For design studies of such facilities, accurate and comprehensive nuclear data of deuteron-induced reactions are indispensable. Toward evaluation of deuteron nuclear data, we have developed a code system dedicated for deuteron-induced reactions, called DEURACS. In DEURACS, breakup processes of incident deuteron are taken into account. DEURACS was so far successfully applied to analyses of production of nucleons, composite particles up to  = 4, and residual nuclei. In this talk, we will present the results of these analyses and discuss how important it is to consider the breakup processes for accurate prediction of deuteron-induced reactions. Moreover, we have recently developed JENDL/DEU-2020, a deuteron nuclear database for
= 4, and residual nuclei. In this talk, we will present the results of these analyses and discuss how important it is to consider the breakup processes for accurate prediction of deuteron-induced reactions. Moreover, we have recently developed JENDL/DEU-2020, a deuteron nuclear database for 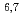 Li,
Li,  Be, and
Be, and 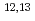 C up to 200 MeV. DEURACS was employed for evaluation of JENDL/DEU-2020. Validation of JENDL/DEU-2020 was carried out by the simulation with the Monte Carlo transport codes. These validation results will also be presented.
C up to 200 MeV. DEURACS was employed for evaluation of JENDL/DEU-2020. Validation of JENDL/DEU-2020 was carried out by the simulation with the Monte Carlo transport codes. These validation results will also be presented.
Haga, Katsuhiro
Kasokuki, 18(4), p.210 - 216, 2022/01
The pulsed spallation neutron source driven by a high-power accelerator is one of the most powerful apparatus to provide high intensity and high quality neutrons with narrow pulse width for conducting cutting-edge researches in several domains of materials and life science. In this system, proton beams of several kW to MW order extracted from the high power accelerator is injected into a target, which is heavy metal, to generate vast amount of neutrons via the spallation reactions with the target nuclei, and slows down these neutrons to thermal to cold neutrons with a moderator and a reflector. Resultant neutron beams are then supplied to a suit of the state-of-the-art experimental devices. In this paper, mechanism to produce neutron beams and outline of the spallation neutron source, engineering design of a target system such as a mercury target, and technical topics to solve the pitting damage problem of the target vessel which is caused by the pressure wave of up to 40MPa at maximum generated in the mercury by the pulsed proton beam injection are reviewed by referring mainly to the mercury target system of the pulsed spallation neutron source at J-PARC.
Arai, Masatoshi*; Andersen, K. H.*; Argyriou, D. N.*; Schweika, W.*; Zanini, L.*; Harjo, S.; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Harada, Masahide
Journal of Neutron Research, 23(4), p.215 - 232, 2021/12
Nakamura, Shoji; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Toh, Yosuke; Harada, Hideo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(12), p.1318 - 1329, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The present study performed fast-neutron capture cross-section measurement of  Tc by an activation method using a fast-neutron source reactor "YAYOI" of the University of Tokyo. Technetium-99 samples were irradiated with reactor neutrons using a pneumatic system. Reaction rates of
Tc by an activation method using a fast-neutron source reactor "YAYOI" of the University of Tokyo. Technetium-99 samples were irradiated with reactor neutrons using a pneumatic system. Reaction rates of  Tc were obtained by measuring decay gamma rays emitted from
Tc were obtained by measuring decay gamma rays emitted from  Tc. The neutron flux at an irradiation position was monitored with gold foils. The fast-neutron capture cross section of
Tc. The neutron flux at an irradiation position was monitored with gold foils. The fast-neutron capture cross section of  Tc at neutron energy of 85 keV was derived as 0.432
Tc at neutron energy of 85 keV was derived as 0.432 0.023 barn by using the reaction rates of
0.023 barn by using the reaction rates of  Tc, evaluated cross-section data and the fast-neutron flux spectrum of the YAYOI reactor. The present study agreed with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-4.0.
Tc, evaluated cross-section data and the fast-neutron flux spectrum of the YAYOI reactor. The present study agreed with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-4.0.
Nakashima, Hiroshi; Nakamura, Takemi; Kobayashi, Hitoshi*; Tanaka, Susumu*; Kumada, Hiroaki*
NEA/NSC/R(2021)2 (Internet), p.142 - 151, 2021/12
Aiming of development of facilities for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) that can be installed in hospitals, an accelerator-based BNCT facility is being developed at the Ibaraki Neutron Medical Research Center under a collaboration among the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, the High Energy Accelerator Research Organization, the University of Tsukuba, and other institutions. It consists of a proton accelerator, having a maximum beam power of 80 kW, and a target, moderator, collimator and shield (TMCS) system. For the design concept, to satisfy the BNCT beam conditions and achieve a low activation, the radiation behavior in the TMCS system was simulated by the Monte Carlo method and this system configuration was optimized accordingly. In addition, the radiation estimation of the TMCS system was verified via several experiments and its applicability for BNCT was proved. This report reviews the estimation and validation studies for the development of the accelerator-based BNCT facility.
Takeda, Masayasu
Bunseki, 2021(11), p.611 - 615, 2021/11
no abstracts in English
Hironaka, Kota; Ito, Fumiaki*; Lee, J.; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Takahashi, Tone; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Yogo, Akifumi*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*
Dai-42-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2021/11
Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is a method for non-destructive measurement of nuclear material by using a time-of-flight (TOF) technique with a pulsed neutron source. For NRTA system to carry out the short-distance TOF measurements with high resolutions, a short-pulsed neutron source is required. Laser-driven neutron sources (LDNSs) is very suitable as such a neutron source because of its short pulse width. Moreover, the compactness of the laser system is also expected due to the remarkable development of laser technology in recent years. In the present study, we have developed a technology for applying LDNS to the NRTA system and conducted the demonstration experiment using the LFEX laser at Osaka University to investigate the feasibility of the system. In this experiment, we successfully observed the neutron resonance peaks of indium and silver samples.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita; Okubo, Nariaki; Yuyama, Takahiro*; Ishii, Yasuyuki*
Proceedings of 18th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.296 - 301, 2021/10
no abstracts in English
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(7), p.805 - 821, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:96.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Intensive fast neutron sources using deuteron accelerators have been proposed for various applications. To contribute to the design study of such neutron sources, a deuteron nuclear data library for 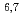 Li,
Li,  Be, and
Be, and 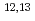 C up to 200 MeV, JENDL/DEU-2020 is developed. The evaluation of JENDL/DEU-2020 are performed by employing the code system DEURACS with particular attention to neutron production data. Toward the evaluation of JENDL/DEU-2020, some modifications are made to DEURACS. The validation of the library is performed though simulation with the Monte Carlo transport calculation codes. From the simulation, it is shown that the calculation results based on JENDL/DEU-2020 reproduce the measured neutron production data well in the incident energies up to 200 MeV. The new library is expected to make a large contribution to diverse design studies of deuteron accelerator neutron sources.
C up to 200 MeV, JENDL/DEU-2020 is developed. The evaluation of JENDL/DEU-2020 are performed by employing the code system DEURACS with particular attention to neutron production data. Toward the evaluation of JENDL/DEU-2020, some modifications are made to DEURACS. The validation of the library is performed though simulation with the Monte Carlo transport calculation codes. From the simulation, it is shown that the calculation results based on JENDL/DEU-2020 reproduce the measured neutron production data well in the incident energies up to 200 MeV. The new library is expected to make a large contribution to diverse design studies of deuteron accelerator neutron sources.
Hidaka, Akihide
Fission Product Behavior under Severe Accident, p.85 - 88, 2021/05
no abstracts in English
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.03014_1 - 03014_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:86.93(Nuclear Science & Technology)Intensive neutron sources using deuteron accelerators have been proposed for various applications such as irradiation test for fusion reactor materials and production of radioisotopes for medical use. In addition, transmutation system using deuteron-induced spallation reactions has been recently proposed for LLFPs. Accurate and comprehensive deuteron nuclear data are indispensable in the design study of such facilities. Under the above situations, we have been developing a code system dedicated for deuteron-induced reactions, which is called DEURACS. In the present work, calculations using DEURACS are compared with available experimental data up to 200 MeV such as DDXs for emission of neutron or light charged particles. We also analyze isotopic production cross sections of residual nuclei. Validation of the present modelling in DEURACS is discussed through comparison with the experimental data.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Oi, Motoki; Fujimori, Hiroshi*
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(6), p.062802_1 - 062802_24, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:36.4(Physics, Nuclear)As hadron accelerators for such as the ADS and spallation neutron source achieve increasing beam power, damage to targets is becoming increasingly severe. To mitigate this damage, nonlinear beam optics based on octupole magnets is attractive. Nonlinear optics can decrease the beam-focusing hazard due to failure of the rastering magnet. As a side effect of nonlinear optics, the beam size is known to expand drastically compared with linear optics. Nonlinear effects have been studied via a simplified filament model that ignores beam-divergence spread at the octupole magnet. In this study, a new generalized model is proposed for application to an octupole magnet, regardless of the filament-model approximation. It is found that the transverse distribution obtained by beam tracking can be specified by the introduction of only two parameters, namely the normalized octupole strength of 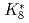 and the
and the 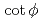 of the phase advance. To achieve the two antagonistic requirements of reduction of the beam-peak density and minimization of the beam loss, the transverse distribution is surveyed for a large range of beam position. It is found that a bell-shaped distribution with
of the phase advance. To achieve the two antagonistic requirements of reduction of the beam-peak density and minimization of the beam loss, the transverse distribution is surveyed for a large range of beam position. It is found that a bell-shaped distribution with 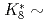 1 and
1 and 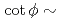 3 can satisfy requirements. This result is applied to beam transport in the spallation neutron source at J-PARC. The calculation result given by the present model shows good agreement with the experimental data, and the peak current density is reduced by 50% compared with the linear-optics case.
3 can satisfy requirements. This result is applied to beam transport in the spallation neutron source at J-PARC. The calculation result given by the present model shows good agreement with the experimental data, and the peak current density is reduced by 50% compared with the linear-optics case.
Xu, P. G.; Ikeda, Yoshimasa*; Hakoyama, Tomoyuki*; Takamura, Masato*; Otake, Yoshie*; Suzuki, Hiroshi
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 53(2), p.444 - 454, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:65.47(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) ZnO using polyethylene by accelerator neutrons
ZnO using polyethylene by accelerator neutronsTsukada, Kazuaki; Nagai, Yasuki*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Minato, Futoshi; Kawabata, Masako*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Watanabe, Satoshi*; Saeki, Hideya*; Motoishi, Shoji*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(3), p.034201_1 - 034201_7, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:22.16(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We found anomalously large yields of  Ga,
Ga, 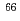 Ga,
Ga, 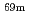 Zn and
Zn and  Cu by neutron irradiation on a
Cu by neutron irradiation on a  ZnO sample in a polyethylene shield. Neutron beams are generated from the
ZnO sample in a polyethylene shield. Neutron beams are generated from the  Be(
Be( ) reaction for 50 MeV deuterons. The yields obtained were more than 20 times larger than those in the unshielded sample. On the other hand, the yields of
) reaction for 50 MeV deuterons. The yields obtained were more than 20 times larger than those in the unshielded sample. On the other hand, the yields of  Ga,
Ga, 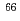 Ga,
Ga, 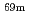 Zn and
Zn and  Cu from a metallic
Cu from a metallic  Zn sample and the yields of
Zn sample and the yields of  Cu,
Cu,  Ni and
Ni and  Zn from the
Zn from the  ZnO and
ZnO and  Zn samples were almost insensitive to the shield conditions. This finding would provide us a unique capability of accelerator neutrons to simultaneously produce a large amount of several radioisotopes, including proton induced reaction products, by using a single sample. The experimental data were compared with the yields estimated by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System and the result was discussed.
Zn samples were almost insensitive to the shield conditions. This finding would provide us a unique capability of accelerator neutrons to simultaneously produce a large amount of several radioisotopes, including proton induced reaction products, by using a single sample. The experimental data were compared with the yields estimated by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System and the result was discussed.